
Selecting automatic door systems demands careful consideration of critical factors. Businesses prioritize performance, safety, and longevity for their investment. Understanding Automatic DoorTop Factors to Consider When Buying Automatic Door Motors is crucial for optimal choices. The industrial automatic door market projects significant growth, from USD 6.2 billion in 2025 to USD 11.3 billion by 2034, at a 6.9% CAGR. The automatic sliding doors market also anticipates steady growth, reaching $3.31 billion in 2030. Navigating options like AC vs DC Automatic Door Motors: Which Is Better? and avoiding Common Mistakes When Purchasing Automatic Door Motors ensures a sound purchase. Knowing How to Evaluate Automatic Door Motor Suppliers in China is also key when selecting Automatic Door Motors and Automatic Door Accessories.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right motor by knowing your door’s use, weight, and environment. Heavy doors need strong motors, and busy areas need durable ones.
- Look at motor types like AC for heavy use or BLDC for quiet and efficient operation. Match the motor’s power to your door’s weight for smooth movement.
- Safety sensors are very important. They stop doors from closing on people or objects. Also, make sure doors have backup power and emergency exits.
- Check for quality by looking at industry certifications and the manufacturer’s reputation. A good warranty and strong materials mean a reliable door.
- Professional installation and regular maintenance keep your automatic door working well. Make sure spare parts are easy to find and good technical support is available.
Understanding Your Application Needs
Traffic Volume and Flow
Understanding the volume and flow of traffic through an automatic door is crucial. Different environments place varying demands on door systems. For instance, facilities like hospitals, retail stores, airports, and hotels experience heavy daily traffic. These doors cycle thousands of times per week, requiring robust motors and quarterly maintenance. Office buildings, banks, and educational campuses represent mid-traffic environments. They have regular but not continuous door use, recommending semi-annual maintenance.
For facilities with lower usage, such as warehouses, administrative offices, and small clinics, low to moderate traffic is typical. Entrances here serve limited-use areas, making annual maintenance sufficient. Businesses with unique operational demands or varying seasonal traffic, like museums and event centers, may need customized plans due to specialized door systems or fluctuating visitor numbers.
Consider these duty classifications:
- Light-Duty: Up to 25 cycles per day, suitable for small commercial, low-traffic areas.
- Medium-Duty: Up to 50 cycles per day, common in retail with moderate traffic.
- Standard-Duty: Up to 75 cycles per day (30 per hour), found in loading docks and warehouses.
- Industrial-Duty: Up to 300 cycles per day, ideal for distribution centers and high-traffic industrial settings.
High-traffic areas, such as retail storefronts, airport entrances, and healthcare corridors, benefit from automatic sliding doors. These doors accommodate simultaneous two-way traffic flow. Full energy swing door operators also suit high traffic, typically for one-way movement. Low energy swing door operators are ideal for light traffic, often used for ADA compliance, activated by a button push.
Door Type and Weight
The physical characteristics of the door significantly influence motor selection. Door type, material, and weight directly impact the required motor power. Heavy doors, such as those made of solid wood or reinforced glass, demand more powerful motors. Lighter doors, like aluminum or hollow core, require less force. Different door mechanisms, including sliding, swing, or revolving doors, each have specific motor requirements. A motor must possess adequate weight capacity to operate the door smoothly and safely over its lifespan.
Environmental Conditions
External environmental factors play a vital role in motor durability and performance. Extreme temperatures, high humidity, dust, and strong winds can degrade motor components. For example, outdoor installations or doors in industrial settings exposed to harsh elements need motors with higher ingress protection (IP) ratings. These ratings indicate resistance to dust and water. Motors designed for specific environmental challenges ensure reliable operation and extend the system’s service life. Selecting motors built to withstand these conditions prevents premature wear and costly repairs.
Key Motor Specifications and Features

Motor Type and Technology
The motor type significantly influences an automatic door system’s performance and longevity. Two primary types dominate the market: AC motors and Brushless DC (BLDC) motors. Each offers distinct advantages for various applications.
| Feature | AC Motors | Brushless DC (BLDC) Motors (Type of DC Motor) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Use | Commercial and industrial automatic doors | Modern, high-end automatic doors |
| Durability | High durability and reliability | Good durability |
| Heavy-Duty Apps | Suitable for heavy-duty applications | Less common for extremely heavy-duty |
| Energy Efficiency | Less energy-efficient | Energy-efficient, consumes less power |
| Noise Level | Louder operation | Quieter operation |
| Speed Control | Limited speed control options | Precise speed and position control |
| Size/Weight | Larger and heavier | Compact and lightweight |
| Initial Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Power Supply | Direct AC power operation | Requires a power supply with DC conversion |
| Maintenance | Simple machines, less prone to electronic issues | Low maintenance (brushless design) |
| Smart Features | Limited options | Integrates with smart control systems |
BLDC motors are often preferred when high efficiency, precise control, and quiet operation are critical. They also offer a compact, lightweight design. Conversely, AC motors suit applications where cost is a primary factor, or where robustness and durability in harsh environments are paramount. They also excel in heavy-duty or continuous operations.
Weight Capacity and Power
A motor’s weight capacity and power directly correlate with the door it operates. The motor must possess sufficient power to move the door smoothly and safely. Different door types require varying power levels.
| Door Type/Weight Capacity | Power Consumption Range |
|---|---|
| Lightweight Roller Doors | 250W to 300W |
| Medium Weight Roller Doors | 350W to 400W |
| Heavy or Industrial Roller Doors | 500W or more |
| Sheet Roller Doors (residential/office) | 300W to 400W |
| Tube Motors (lighter/smaller roller doors) | 250W to 350W |
| Chain-Driven Roller Doors (heavy/industrial) | 500W or higher |
For instance, a 50W swing door opener can effectively handle a door weighing up to 220.46 lbs. Matching the motor’s power to the door’s weight prevents strain on the system and ensures reliable operation.
Opening and Closing Speed
The opening and closing speed of an automatic door impacts both efficiency and safety. High-traffic areas benefit from faster speeds, which minimize waiting times and improve traffic flow. However, excessive speed can compromise safety, especially in environments with children or elderly individuals. Manufacturers design motors to offer adjustable speeds, allowing customization based on specific application needs. This balance between speed and safety is crucial for optimal performance.
Duty Cycle and Durability
A motor’s duty cycle indicates its operational capacity over time. It defines how long a motor can run continuously versus how long it needs to rest. A high duty cycle rating signifies a motor built for frequent and prolonged use, directly impacting its durability and lifespan. Commercial operators, for example, feature continuous-duty motors. Manufacturers engineer these motors to run cooler and for longer durations. They often include features like overload protection and high starting torque, which residential motors typically lack.
These commercial operators are designed for high duty cycles. Standard models handle approximately 30 cycles per hour, while industrial-duty models accommodate up to 300 cycles daily. This robust design contributes to a significant lifespan.
| Specification | Residential Systems | Commercial Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Expected Lifespan | 10-15 years | 10-15 years (with maintenance) |
Proper maintenance helps commercial systems achieve their expected lifespan. Choosing a motor with an appropriate duty cycle for the application ensures long-term reliability and reduces the need for frequent replacements.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
Energy efficiency has become a critical consideration for automatic door motors. Efficient motors consume less power, leading to lower operating costs and a reduced environmental footprint. Manufacturers of automatic sliding door motors increasingly align their products with energy efficiency standards and certifications. This compliance ensures the motors meet specific energy performance criteria, offering a reliable benchmark for consumers to select energy-efficient options.
Several codes and requirements guide energy efficiency in automatic door systems:
- ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act)
- IBC (International Building Code)
- IECC (International Energy Conservation Code)
- ANSI 156.19 or 156.10 (depending on location and building type)
Energy efficiency goals also include improved thermal performance, measured by U-factor and SHGC (Solar Heat Gain Coefficient), and air infiltration, tested by ASTM E283. These factors are important considerations for door specification, helping to minimize heat loss or gain through the door system. Selecting motors that meet these standards contributes to overall building energy savings.
Essential Automatic Door Accessories

Automatic door systems rely on various accessories to enhance safety, security, and functionality. These components work together with the motor to provide a complete and efficient door solution. Selecting the right Automatic Door Accessories is as important as choosing the motor itself.
Safety Sensors and Detection
Safety sensors are critical Automatic Door Accessories. They prevent accidents and ensure safe operation for all users. These sensors detect people or objects in the door’s path, stopping or reversing its movement to avoid collisions. Common types of safety sensors include:
- Motion Sensors: These sensors detect movement using radar or microwave technology. They trigger the door to open when someone approaches.
- Infrared Sensors: These sensors detect changes in heat or body temperature near the doorway. They allow for contactless operation.
- Safety Beam Sensors (Photoelectric Beams): These project an invisible light beam across the doorway. If someone breaks the beam, the door stops or reverses its action.
- Pressure or Floor Sensors: Installed under the flooring, these sensors detect weight changes when someone steps on a mat.
- Combination Sensors: These integrate multiple motion and safety sensors. They offer improved reliability and meet safety compliance standards.
Access Control Integration
Integrating automatic doors with access control systems enhances security and manages entry. This integration allows only authorized individuals to pass through the door. The process typically involves an employee presenting an access credential to a door reader. This reader connects to an Access Control Unit (ACU). The ACU validates the credential. It then sends a signal to the automatic door opener. This signal unlocks the door’s locking device, such as an electric strike or electromagnetic lock. The automatic door opener then opens the door. It closes the door after a set time, usually 5-10 seconds. Common integration protocols include RS485, Wiegand, and TCP/IP.
Power Backup Systems
Power backup systems are vital Automatic Door Accessories. They ensure continued operation during power outages. An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) system provides temporary power to the automatic door. This allows people to exit or enter the building safely. UPS systems can offer a runtime of 1–2 hours or more. The duration depends on the system’s configuration and battery capacity. Some systems can power an access control system for approximately 4–12 hours. Municipalities often size UPS systems to power traffic signals for 2–6 hours. This principle also applies to commercial buildings.
Control Panels and Switches
Control panels and switches serve as the central interface for managing automatic door systems. They allow users to operate doors, adjust settings, and monitor performance. For commercial applications, these panels offer advanced functionalities crucial for security and operational efficiency. Essential features of an automatic door control panel for commercial use include:
- Role-Based Access Permissions: The system assigns access rights based on job functions and organizational hierarchy. This ensures sensitive areas remain restricted to authorized personnel.
- Centralized Access Management: It consolidates all access control functions into a single platform. This allows management of multiple locations and users from one dashboard.
- Entry and Exit Activity Logs: The system creates detailed records of all door activity. These logs include successful entries, denied attempts, and status changes, useful for investigations and compliance.
- Time-Based Access Controls: It limits access to specific hours, days, or date ranges. This automatically enforces security policies and manages temporary access.
- Remote Access Management: Administrators can control access systems from anywhere using web-based or mobile applications. This facilitates emergency responses and multi-location management.
- System Integrations: The panel connects access control with other security technologies like video surveillance and alarms. This provides coordinated responses and comprehensive security coverage.
These sophisticated control panels are vital Automatic Door Accessories, enhancing both security and convenience.
Emergency Release Mechanisms
Emergency release mechanisms are critical Automatic Door Accessories. They ensure safe egress during power failures or other emergencies. These mechanisms allow doors to open manually, even if the automatic system fails. Automatic doors must include features for safe emergency egress, such as manual release mechanisms and battery backups.
Various safety regulations govern these mechanisms to protect occupants.
- ANSI/BHMA A156.10 Compliance: Power-operated pedestrian doors (excluding low-energy) must comply with ANSI/BHMA A156.10. This standard defines ‘Break Away Device’ (emergency release) and ‘Break Out’ (activating the device).
- Break Out Force Limit: The BHMA standard and model codes limit the opening force for the break out feature to 50 lbf. This force applies 1 inch from the leading edge of the lock stile.
- NFPA 101 (2024) – Life Safety Code: This code requires a ‘swing-out feature’. The door leaf must swing from any position to provide the full required opening width when force applies from the egress side.
- International Building Code (IBC) (2024): Section 1010.3.2 mandates power-operated doors to swing in the direction of egress during an emergency. The door must open to its full width from any position when force applies from the egress side.
- Clear Opening Width: Both I-Codes and NFPA codes have exceptions regarding the 32-inch minimum clear opening width for a single leaf. I-Codes require a total of 32 inches clear opening width (both leaves when broken out). NFPA codes require each leaf to provide at least 30 inches clear.
These regulations ensure that automatic doors provide reliable emergency exits, prioritizing occupant safety.
Evaluating Quality and Reliability
Industry Certifications and Standards
Automatic door systems require adherence to strict industry certifications and standards. These guidelines ensure the safety, performance, and reliability of the products. Compliance with standards like ANSI/BHMA A156.10 for power-operated pedestrian doors or UL certifications for electrical safety indicates a manufacturer’s commitment to quality. These certifications provide assurance that the motor and its components meet rigorous testing requirements. They also confirm the system operates safely in various environments. Always verify a product’s certifications before making a purchase decision.
Manufacturer Reputation and Warranty
A manufacturer’s reputation directly reflects the quality and reliability of its automatic door motors. Reputable companies often have a long history of producing durable and high-performing products. They also stand behind their offerings with comprehensive warranties. These warranties protect your investment against defects in materials and workmanship.
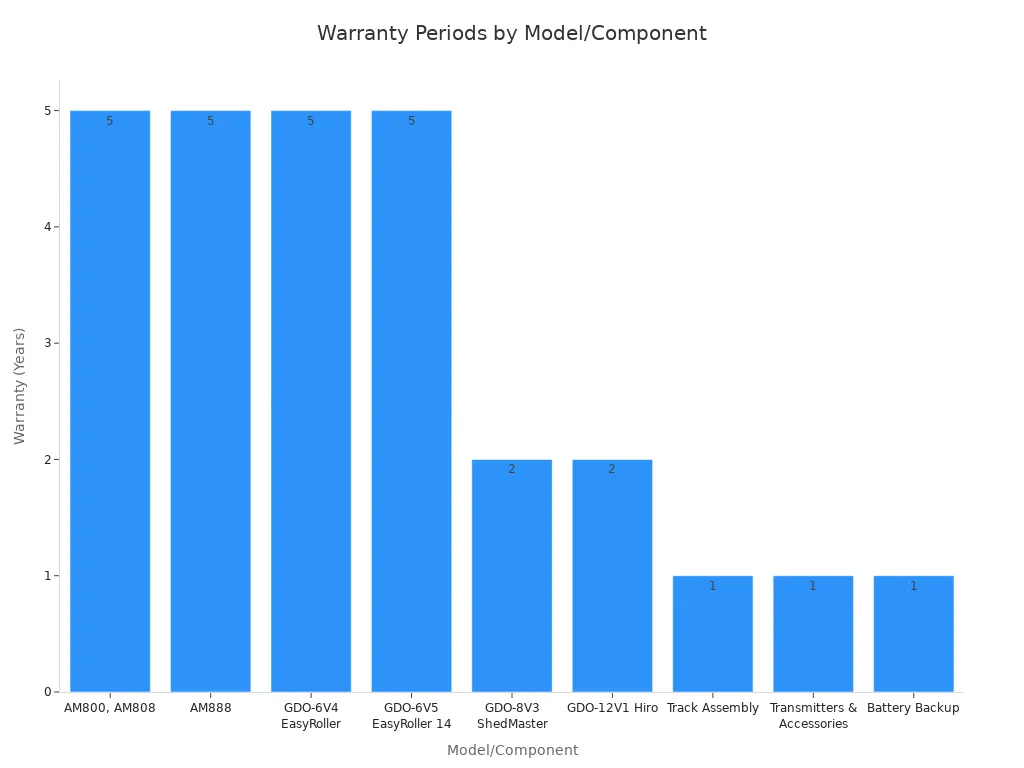
Manufacturers offer varying warranty periods for different components. For example, motor and parts warranties for sectional doors like the AM800 or AM888 typically extend for five years or 10,000 cycles. Rolling door models such as the GDO-6V4 EasyRoller also carry a five-year or 10,000-cycle warranty. However, some models like the GDO-8V3 ShedMaster offer a two-year or 5,000-cycle warranty. Accessories and track assemblies usually come with a one-year warranty.
| Model/Component | Warranty (Motor & Parts) |
|---|---|
| SECTIONAL | |
| AM800, AM808 | 5 Years / 10,000 cycles |
| AM888 | 5 Years / 10,000 cycles |
| ROLLING | |
| GDO-6V4 EasyRoller | 5 Years / 10,000 cycles |
| GDO-6V5 EasyRoller 14 | 5 Years / 10,000 cycles |
| GDO-8V3 ShedMaster | 2 Years / 5,000 cycles |
| GDO-12V1 Hiro | 2 Years / 10,000 cycles |
| EXTRAS | |
| Track Assembly (includes all parts) | 1 Year |
| Transmitters & Accessories | 1 Year |
| Battery Backup | 1 Year |
Manufacturer warranties for automatic gate openers typically range from one to five years. They cover defects in materials and workmanship. Some manufacturers offer limited lifetime warranties on specific components, such as the motor or frame. Different parts often have varying warranty periods. For instance, the motor might have a longer warranty (e.g., 5 years) compared to electronic components (e.g., 1-2 years).
Material Quality and Construction
The quality of materials and construction significantly impacts an automatic door motor’s lifespan and performance. High-grade materials ensure durability and resistance to wear and tear. For example, motor housings typically consist of high-quality plastic. Drive nuts and gears can be made from metal or plastic, with metal offering greater strength.
A DC motor’s stator contains permanent magnets. Its rotor consists of silicon steel laminate, a motor shaft, a commutator, and copper windings. Carbon brushes, also part of DC motors, are made of carbon. These components must withstand continuous operation and environmental stresses. Superior construction techniques, such as precision engineering and robust assembly, minimize the risk of breakdowns. They also ensure smooth, quiet operation over many years.
User Reviews and Case Studies
User reviews and case studies offer invaluable insights into the real-world performance and reliability of automatic door motors and accessories. These resources provide perspectives beyond manufacturer specifications. They help potential buyers make informed decisions.
User reviews often highlight practical aspects of product ownership. Customers share their experiences with installation, daily operation, and maintenance. They discuss the product’s durability and how well it meets their specific needs. For example, a review might praise a motor’s quiet operation or its ability to withstand heavy traffic. Conversely, it might point out issues with customer support or unexpected repair costs. These firsthand accounts offer a realistic view of a product’s strengths and weaknesses.
Case studies provide a more detailed examination of how automatic door systems perform in specific environments. These studies often document the entire process, from initial selection to long-term operation. They include data on energy efficiency, operational uptime, and return on investment. A case study might showcase how a particular motor system improved traffic flow in a busy retail store. It could also demonstrate how a specific accessory enhanced security in a corporate building. These detailed reports offer concrete evidence of a product’s effectiveness and value.
Businesses should actively seek out these testimonials and reports. They offer a crucial layer of validation for product claims. Analyzing multiple reviews and case studies helps identify consistent patterns. This process reveals common issues or recurring benefits. It allows buyers to assess a product’s suitability for their own application. Ultimately, real-world feedback from other users and documented successes in case studies build confidence in a purchasing decision. They ensure the chosen automatic door system will perform as expected.
Considering Installation and After-Sales Support
The long-term success and safety of an automatic door system depend heavily on its installation and the support it receives afterward. Businesses must prioritize these aspects to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Professional Installation Requirements
Professional installation is paramount for automatic door systems. It ensures proper functionality and adherence to safety standards. Installers calibrate motion and safety sensors precisely, adjust opening and closing speeds, and integrate fire and emergency systems. They also ensure compliance with energy codes. After installation, the provider issues a certification of compliance and schedules periodic inspections. When selecting a system, consider the activation method, such as motion sensors or touchless panels, and the door material. Energy efficiency, safety compliance with standards like ANSI/BHMA A156.10, and the brand’s reputation are also crucial. Installers must carefully manage wiring and electrical setups, avoiding hazard zones and shielding wires with conduit. They install motion sensors at the correct height, typically 6-7 feet above the door, and aim them for the approach zone. Safety beams are placed near the floor, about 6-10 inches high. Finally, programming and testing fine-tune speed and hold settings for safety and responsiveness.
Maintenance and Service Plans
Regular maintenance is essential for automatic door motors, especially in high-traffic environments. High-traffic facilities often schedule commercial door maintenance quarterly. Some organizations even require monthly inspections. A full professional inspection is recommended at least annually. In-house visual checks and lubrication of moving parts should occur quarterly. For high-cycle commercial doors in dusty environments, monthly checks are vital. BLDC (Brushless DC) automatic door motors have low maintenance requirements because their brushless design eliminates the need for brush replacement. A helical gear transmission further ensures smooth and stable operation, minimizing mechanical issues and downtime.
| Maintenance Tier | Service Life (hours) | Key Procedures |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Maintenance | 2,000-5,000 | Visual inspections, routine cleaning, brush replacement at wear limit. |
| Standard Maintenance | 5,000-10,000 | Detailed inspections, deep cleaning, in-situ resurfacing, brush pressure verification. |
| Premium Maintenance | 10,000-20,000 | Detailed inspections, deep cleaning, proactive resurfacing, brush pressure checks, machine shop reconditioning. |
Availability of Spare Parts
The availability of spare parts significantly impacts the long-term cost and operational efficiency of automatic door systems. Brand and door type influence part availability. Sliding doors generally have more readily available parts due to their commonality. In contrast, revolving doors are more complex and often require specialized servicing, which can make repairs more expensive. Furthermore, some automatic door brands utilize proprietary parts. This means finding compatible components might necessitate sourcing from specific vendors, potentially leading to longer lead times and higher costs.
Technical Support and Troubleshooting
Reliable technical support and efficient troubleshooting are crucial for maintaining automatic door systems. Even the most robust systems can encounter issues, and prompt, expert assistance minimizes downtime. Providers offer various support channels to help customers. These services often include assistance with installation and setup, ensuring correct initial configuration. They also provide troubleshooting and maintenance guidance, which helps resolve operational problems quickly. Furthermore, many companies offer training and education, empowering users to understand and manage their systems better.
Customers can typically access support through several convenient methods. Many providers feature a dedicated support link on their websites, offering a gateway to resources and contact options. For those needing direct interaction, a "Talk to our sales team" option often connects them with knowledgeable representatives. Some companies also encourage customers to "Get in Touch with an Expert" for specialized advice. A general "Contact Us" link provides various communication methods, including phone and email. For immediate assistance, a live chat feature has become a common offering, allowing real-time problem-solving. These diverse channels ensure customers receive the help they need, when they need it, keeping their automatic doors functioning smoothly and safely.
Budgeting and Value for Money
Initial Purchase Cost
The initial purchase cost for an automatic door system is a significant factor. Businesses must consider this investment carefully. Full automatic operators, like those in grocery stores or airports, typically cost between $7,000 and $12,000 per door. This price includes the motor, door panels, and basic installation. The specific door type, size, and features also influence the overall cost. Higher-end systems with advanced security or aesthetic features will naturally have a higher upfront price.
Long-Term Operating Expenses
Long-term operating expenses are crucial for evaluating the true cost of an automatic door system. These expenses include energy consumption and maintenance. Automatic doors use electricity, but their power usage is generally minimal compared to other building systems. However, poorly sealed doors can significantly increase HVAC costs. They allow conditioned air to escape, impacting energy efficiency.
Regular maintenance is also a key expense. This includes:
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning is necessary, especially for glass doors in retail or food service settings. This maintains their appearance.
- Hardware Servicing: Components like hinges, door closers, locks, and automation systems require periodic inspection and adjustment. Higher-quality hardware typically offers a longer service life.
- Repairs and Part Replacements: Wear and tear are inevitable. This leads to costs for replacing damaged parts like door closers or automatic sensors. These replacements can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars. Economical doors often use lower-grade parts. These parts may require earlier replacement.
Return on Investment
Evaluating the return on investment (ROI) for an automatic door system involves more than just initial and operating costs. Businesses should consider the benefits these doors provide. Automatic doors enhance customer experience. They improve accessibility for all users. They also contribute to energy savings through better climate control. A well-chosen system can reduce staff workload. It can also increase security. These factors contribute to a positive ROI over the system’s lifespan. Investing in a durable, energy-efficient system with good support often yields better long-term value.
Customization Options and Scalability
Automatic door systems offer extensive customization options. Businesses can tailor these systems to meet specific operational and aesthetic requirements. This ensures the doors integrate seamlessly into any environment. Customization includes various door materials, finishes, and colors. For example, a high-end retail store might choose sleek glass doors with brushed stainless steel frames. A hospital might opt for durable, easy-to-clean materials. These choices enhance the building’s overall design and brand image.
Beyond aesthetics, functional customization is crucial. Businesses can select specific sensor types. They might choose motion sensors for high traffic or touchless activation for hygiene-sensitive areas. Integration with advanced access control systems allows for secure entry. Specialized operational modes, such as "hold open" for deliveries or "one-way traffic" for events, further enhance functionality. These tailored features optimize door performance for unique application needs.
Scalability refers to a system’s ability to grow or adapt with a business. A well-chosen automatic door system can accommodate future expansion. It can integrate with new technologies. For instance, a business might initially install basic automatic doors. Later, it can upgrade them with advanced security features or smart building management integration. This modular approach allows businesses to invest in a system that evolves with their needs. It avoids costly replacements in the future. Scalable systems provide long-term value and flexibility. They ensure the automatic doors remain efficient and relevant as business requirements change.
Selecting automatic door systems requires careful evaluation of several critical factors. Businesses must consider traffic volume, motor specifications, and essential accessories. They also need to assess product quality, installation support, and overall budget. A holistic approach ensures optimal performance and longevity. Informed decisions lead to safe, efficient, and reliable automatic doors. This comprehensive strategy maximizes the value of the investment.
FAQ
What is the main difference between AC and BLDC automatic door motors?
BLDC motors offer higher energy efficiency, quieter operation, and precise control. AC motors are more robust for heavy-duty applications and have a lower initial cost. Each type suits different operational needs.
How frequently should businesses maintain automatic door systems?
Maintenance frequency depends on traffic volume. High-traffic areas require quarterly checks. Mid-traffic environments need semi-annual service. Low-traffic doors can have annual maintenance. Regular checks ensure longevity.
What are essential safety accessories for automatic doors?
Essential safety accessories include motion sensors, infrared sensors, and safety beam sensors. These components detect people or objects. They prevent collisions. Emergency release mechanisms also ensure safe egress during power failures.
Can automatic doors help reduce energy costs?
Yes, automatic doors can reduce energy costs. They minimize conditioned air loss. Energy-efficient motors consume less power. Proper sealing and compliance with energy codes further enhance savings. This contributes to a positive ROI.